Your emails are landing in Gmail spam folders and you have no idea why. You check your campaigns, tweak your subject lines, clean your lists, but Gmail still treats your messages like junk. Without visibility into how Gmail sees your sending domain, you’re flying blind. Business owners and marketers lose thousands of dollars in missed opportunities because their perfectly good emails never reach their prospects.
Google Postmaster Tools gives you direct access to the metrics Gmail uses to judge your sender reputation. This free dashboard shows you exactly why your emails get filtered, what your spam complaint rate looks like, and whether your authentication passes. You get real data instead of guesswork.
This guide walks you through the complete setup process and shows you how to use each dashboard to improve your Gmail deliverability. You’ll learn how to meet Gmail’s sender requirements, verify your domain, read the metrics that matter, fix common problems, and use this data to improve your marketing results. By the end, you’ll know exactly where you stand with Gmail and what to do about it.
Why Google Postmaster Tools matters for Gmail deliverability
Gmail controls over 1.8 billion email accounts and uses sophisticated filters to protect users from spam. Your sender reputation with Gmail determines whether your emails reach the inbox or get buried in spam folders. Google Postmaster Tools gives you direct access to the exact metrics Gmail uses to evaluate your emails, removing all guesswork from your deliverability strategy.

Your visibility into Gmail’s filtering decisions
You get seven distinct dashboards that show real-time data about how Gmail treats your domain. The spam rate dashboard reveals what percentage of recipients mark your emails as spam. Your domain reputation score shows whether Gmail classifies you as a trusted sender or potential threat. Authentication dashboards confirm whether your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records pass Gmail’s security checks.
Most email platforms show you surface-level metrics like open rates and click rates. Google Postmaster Tools shows you infrastructure-level data that actually affects delivery. You see delivery errors with specific reasons for bounces and blocks. The IP reputation dashboard tracks the health of your sending infrastructure across different email campaigns.
Without this visibility, you’re optimizing blind and wasting money on campaigns that never reach their targets.
The cost of ignoring your sender reputation
Gmail’s February 2024 requirements created strict spam rate thresholds for bulk senders. Senders who exceed 0.3% spam complaints face automatic filtering and potential blocks. Your business loses qualified leads when your emails hit spam folders instead of inboxes. Marketing campaigns fail because prospects never see your offers, not because your messaging is weak.
Authentication failures create immediate deliverability problems. Gmail rejects or quarantines emails that fail DMARC alignment checks or lack proper SPF records. Domain reputation damage takes months to repair once Gmail flags you as a problematic sender. You waste your email service provider fees on messages that Gmail automatically filters before recipients even have a chance to engage.
Google postmaster tools shows you these problems before they destroy your campaigns. You catch authentication issues on day one instead of discovering them after thousands of failed deliveries.
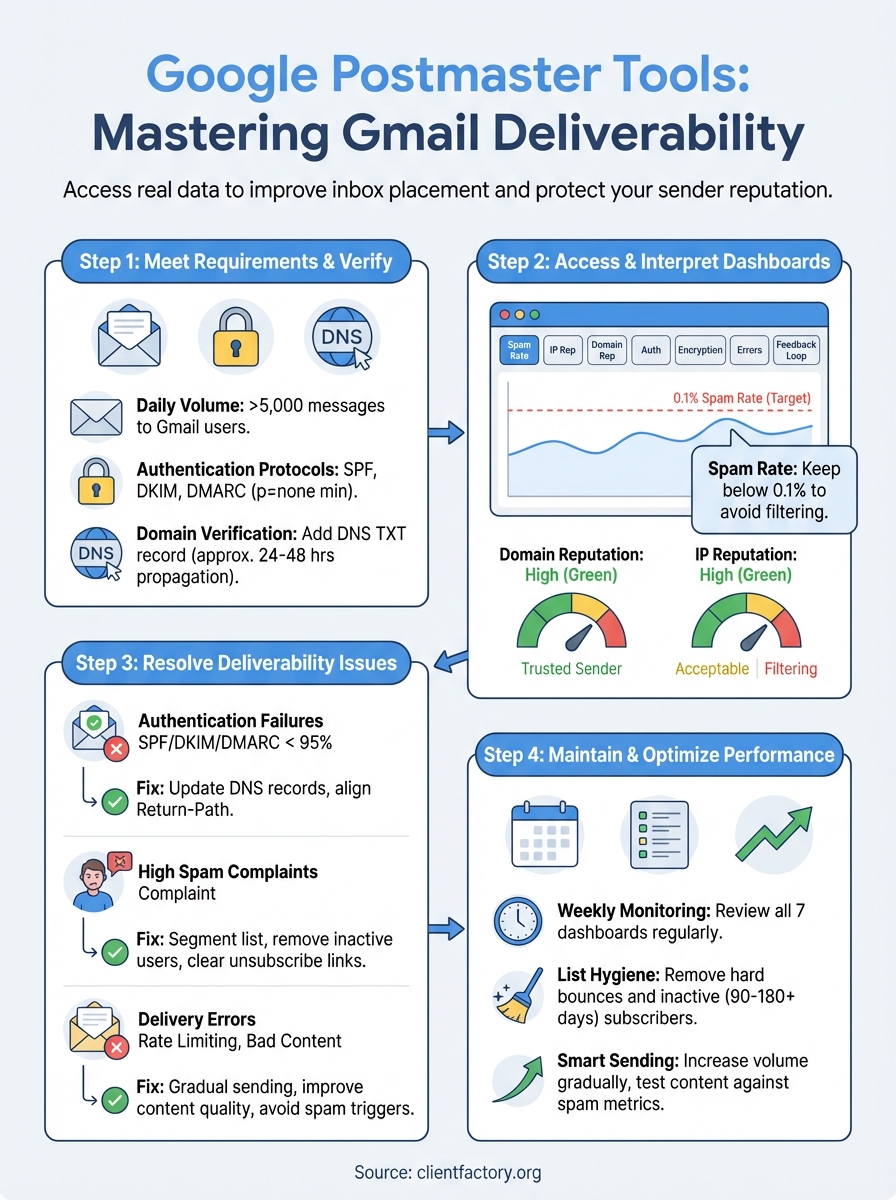
Step 1. Meet Gmail sender and volume requirements
Google postmaster tools only works for senders who meet specific volume thresholds and follow Gmail’s authentication standards. You need to verify your sending practices match Gmail’s requirements before you can access any dashboard data. Your domain must send enough email to Gmail users for the system to collect meaningful metrics about your sender behavior.
Check if you qualify as a bulk sender
Gmail defines bulk senders as anyone who sends more than 5,000 messages per day to Gmail addresses within a 24-hour period. This count includes all messages from your authenticated domain, whether they’re marketing emails, transactional notifications, or automated system messages. You aggregate all sending across your entire domain and any subdomains you use for email campaigns.
Your business crosses this threshold faster than you might expect. A single email campaign to 6,000 subscribers puts you in bulk sender territory. Multiple campaigns throughout the day from different teams or departments combine into your total volume. Automated welcome series, abandoned cart emails, and password resets all count toward your daily sending limit.
Once you send 5,000+ messages per day to Gmail users, you must comply with Gmail’s bulk sender requirements or risk automatic filtering.
Set up authentication before accessing data
You must implement three authentication protocols before Gmail collects data on your domain. SPF (Sender Policy Framework) verifies that your sending IP addresses have permission to send mail for your domain. DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) adds a cryptographic signature to your emails that proves they haven’t been altered in transit. DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication) tells Gmail what to do with emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks.

Add these DNS records through your domain registrar or hosting provider:
SPF record: v=spf1 include:_spf.yourmailprovider.com ~all
DKIM record: Your ESP provides this unique key
DMARC record: v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc@yourdomain.com
Gmail requires at least p=none for your DMARC policy, which monitors authentication without rejecting failed messages. Your Return-Path domain must align with your From domain for proper DMARC authentication. Check your email service provider’s documentation for the exact SPF include statement and DKIM key values you need.
Meet the minimum volume threshold
Your domain needs to send more than 100 authenticated messages per day to Gmail users before data appears in your dashboards. Gmail aggregates this data and updates your metrics once daily, usually reflecting the previous day’s sending activity. Lower volumes don’t generate enough statistical significance for Gmail to display reputation scores or spam rates.
Plan your verification timing around a scheduled campaign or increase your daily sending gradually until you hit the threshold. You won’t see data immediately after adding your domain. Wait 48 to 72 hours after your first high-volume day for metrics to populate across all dashboards.
Step 2. Add and verify your domain with Google
You need to prove you control your sending domain before Google postmaster tools displays any data. The verification process uses DNS records to confirm domain ownership, identical to how you verify domains for Google Search Console or Google Workspace. This one-time setup takes 15 to 30 minutes depending on how quickly your DNS provider propagates changes.
Access the verification interface
Navigate to postmaster.google.com and sign in with any Google account. You don’t need a Gmail address or Google Workspace subscription. Click the blue plus button in the bottom-right corner to open the domain addition dialog. Enter your sending domain exactly as it appears in your email From addresses.

Your choice between root domain and subdomain affects how Google aggregates your data. Add yourdomain.com to see combined metrics across all subdomains and IPs. Add mail.yourdomain.com separately to track specific sending streams independently. Most senders start with their root domain for overall visibility.
Complete the DNS verification process
Google generates a unique TXT record you must add to your domain’s DNS settings. Copy the verification string that looks like google-site-verification=xyz123abc. Access your DNS management panel through your domain registrar, hosting provider, or DNS service. Create a new TXT record with these values:
Type: TXT
Name: @ (or leave blank)
Value: google-site-verification=xyz123abc
TTL: 3600 (or default)
Save the DNS record and return to the Google Postmaster interface. Click Verify to complete the process. Google checks your DNS records immediately and confirms verification within seconds if the record published correctly.
DNS propagation can take up to 48 hours, but most providers update within 15 minutes.
Alternative CNAME verification works if your DNS provider restricts TXT records. Follow the CNAME instructions Google provides as your secondary verification method.
Step 3. Find your way around the dashboards
Google postmaster tools organizes your deliverability data into seven separate dashboards, each tracking a specific aspect of how Gmail handles your emails. You access these dashboards from the left sidebar after selecting your verified domain. The interface updates once per day with metrics from the previous 24 hours, giving you a rolling view of your sending performance over time.
Navigate between dashboard views
Click your verified domain from the main screen to reveal the dashboard navigation menu on the left side. Each dashboard name describes the metric it tracks: Spam rate, IP reputation, Domain reputation, Authentication, Encryption, Delivery errors, and Feedback loop. The date selector at the top lets you choose your time range from the past 120 days, helping you spot trends and correlation between your sending behavior and reputation changes.
Your dashboard displays data only after you reach the minimum volume threshold of 100+ authenticated messages per day to Gmail users. Empty graphs mean either insufficient volume or recent domain addition. Wait 48 to 72 hours after your first qualifying send for metrics to populate across all views.
Interpret your spam complaint rates
The spam rate dashboard shows the percentage of recipients who marked your emails as spam after they reached the inbox. Gmail calculates this rate by dividing spam complaints by total delivered messages to engaged users. You see a line graph with your daily spam rate plotted over your selected time range.
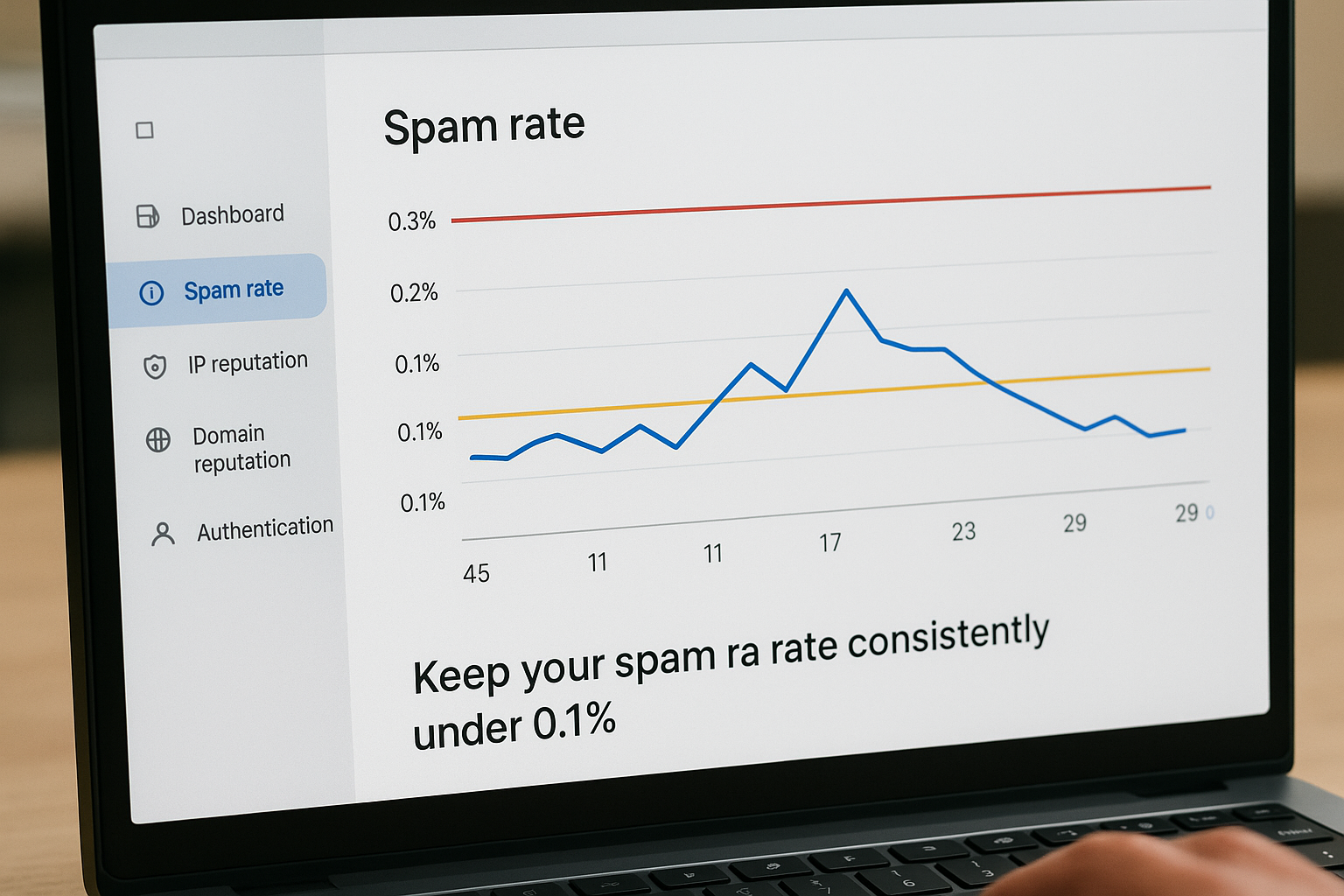
Gmail’s bulk sender requirements mandate keeping your spam rate below 0.3%, with a recommended target under 0.1%. Your graph displays warning thresholds at these levels. Rates above 0.3% trigger automatic filtering and potential blocks from Gmail’s systems.
Keep your spam rate consistently under 0.1% to maintain optimal deliverability and avoid Gmail’s enforcement actions.
Decode reputation color codes
Both your domain and IP reputation dashboards use the same color-coded system to rate your sender quality. Green (High) means Gmail trusts your sending and delivers your emails to the inbox. Yellow (Medium) indicates occasional spam issues with generally acceptable deliverability. Red (Low or Bad) signals serious problems that cause Gmail to filter most of your mail to spam.
Your domain reputation reflects how Gmail views your entire sending domain based on user engagement, spam complaints, and authentication. IP reputation tracks the specific servers you use to send email. Shared sending infrastructure means your IP reputation fluctuates based on other senders using the same servers, while dedicated IPs give you direct control over your reputation scores.
Track both metrics together to identify whether deliverability problems stem from your content and targeting (domain reputation) or your sending infrastructure (IP reputation). Sudden drops in either score require immediate investigation and corrective action before Gmail blocks your messages completely.
Step 4. Fix common Gmail deliverability problems
Google postmaster tools reveals the exact problems blocking your emails from Gmail inboxes. Your dashboards show specific error patterns, authentication failures, and reputation damage that need immediate fixes. You address these issues systematically by starting with critical authentication problems, then moving to spam complaints and delivery errors. Each problem category requires different corrective actions based on what your dashboard data reveals.
Resolve authentication failures
Your authentication dashboard shows three separate pass rates for SPF, DKIM, and DMARC protocols. Rates below 95% indicate configuration problems that cause Gmail to reject or filter your messages. Check your DNS records first when you see authentication failures, because incorrect or missing records create instant deliverability problems across all your campaigns.
SPF failures happen when your sending IPs aren’t authorized in your DNS record. Access your DNS management panel and verify your SPF record includes all legitimate sending sources:
v=spf1 include:_spf.mailprovider.com include:_spf.crm.com ip4:123.45.67.89 ~all
Add each email service provider and third-party sender you use through separate include statements or IP addresses. Test your configuration at mxtoolbox.com/spf.aspx before sending production email. Replace the soft fail (~all) with hard fail (-all) only after you confirm all legitimate sources pass authentication.
DKIM failures mean your email signature doesn’t match or your private key expired. Contact your email service provider to generate a new DKIM key pair and update your DNS with the public key they provide. Your DMARC policy determines what Gmail does with failed messages. Change your policy from p=none to p=quarantine after you fix authentication issues and maintain clean metrics for 30 days.
Lower your spam complaint rate
Spam rates above 0.3% trigger automatic filtering and blocks from Gmail’s systems. Your spam rate dashboard shows you crossed the threshold and need immediate intervention to prevent permanent reputation damage. You reduce complaints by fixing three root causes: irrelevant content, poor list hygiene, and missing unsubscribe options.
Segment your email list based on actual engagement data from the past 90 days. Remove subscribers who haven’t opened your emails in six months or longer, because disengaged recipients generate most spam complaints. Create separate segments for active buyers, newsletter readers, and dormant users. Send targeted campaigns to each segment instead of blasting your entire list with identical content.
Add a visible unsubscribe link in every email header and footer to give recipients an easy exit before they mark you as spam.
Your unsubscribe process must complete in two clicks maximum without requiring login credentials or personal information. Process unsubscribe requests within 24 hours and remove those addresses from all future campaigns. Monitor your feedback loop dashboard to identify which specific campaigns or sender addresses generate the highest complaint rates.
Clean up delivery error patterns
Your delivery errors dashboard lists specific reasons Gmail rejected or temporarily failed your messages. Each error type requires a targeted fix based on the underlying cause. Rate limit errors mean you’re sending too much volume too quickly, while reputation errors indicate Gmail flagged your domain or IP as problematic.
Address rate limiting by spreading your sends across longer time periods. Instead of sending 50,000 emails in one hour, distribute them over 12 to 24 hours. Use your email platform’s throttling settings to control maximum messages per minute and avoid triggering Gmail’s velocity filters. Reduce your daily volume by 30% to 50% until rate limit errors disappear from your dashboard.
Bad attachment errors mean you’re sending file types Gmail blocks for security. Replace executable files (.exe, .bat, .cmd) with safe document formats like PDF. Compress multiple files into password-protected ZIP archives and include the password in your email body. Spam content errors require you to rewrite your subject lines and body copy to avoid trigger words like “free,” “guarantee,” and excessive punctuation marks.
Step 5. Keep your Gmail sender reputation strong
Your sender reputation requires consistent maintenance to stay in Gmail’s good graces. You can’t check google postmaster tools once and forget about it. Your domain and IP reputation scores fluctuate based on daily sending behavior, subscriber engagement, and complaint rates. Build a routine that catches problems early and reinforces positive sending patterns Gmail rewards with better inbox placement.
Monitor your metrics weekly
Schedule a specific day each week to review all seven dashboards in your Postmaster account. Track your spam rate first because it provides the earliest warning signal for deliverability problems. Record your domain reputation color and any changes from the previous week. Check your authentication pass rates to catch configuration drift before it causes widespread failures.
Create a simple tracking spreadsheet with these columns:
| Date | Spam Rate | Domain Rep | IP Rep | SPF Pass % | DKIM Pass % | DMARC Pass % | Delivery Errors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025-12-15 | 0.08% | High | High | 99.2% | 98.8% | 99.1% | 12 |
| 2025-12-08 | 0.06% | High | Medium | 99.5% | 99.1% | 99.3% | 8 |
Your historical data reveals trends that single snapshots miss. A gradual upward trend in spam complaints signals audience fatigue with your messaging frequency or content. Drops in authentication rates indicate DNS problems or misconfigured sending infrastructure that need immediate attention.
Set calendar alerts for your weekly reviews and treat them as non-negotiable appointments for your email program health.
Build gradual sending patterns
Gmail penalizes sudden volume spikes because they mirror spam behavior patterns. Your domain establishes a normal sending baseline over weeks and months. Jumping from 5,000 daily emails to 50,000 overnight triggers automatic scrutiny regardless of your content quality or subscriber permission levels.
Increase your sending volume by no more than 20% per week when scaling campaigns. Start new promotional calendars with smaller segments and expand gradually as Gmail recognizes your consistent positive engagement. Spread large sends across multiple hours instead of dumping your entire list through the system in 30 minutes.
Maintain steady sending frequency even during slow periods. Sending 1,000 emails per day consistently builds better reputation than alternating between 10,000 emails one week and zero the next. Your irregular patterns make Gmail’s algorithms treat you like a new unknown sender instead of a trusted source.
Maintain list quality standards
Your subscriber list quality directly determines your Gmail reputation scores. Remove hard bounces immediately after each campaign because sending to invalid addresses damages your reputation with every attempt. Suppress unengaged subscribers who haven’t opened your emails in 90 to 180 days depending on your typical sending frequency.
Implement double opt-in for all new subscribers to verify email addresses and confirm genuine interest. Send a welcome email immediately after signup and remove addresses that bounce on first contact. Monitor your spam complaints by campaign type to identify which content categories generate the most negative feedback.
Build a suppression list that includes:
- Hard bounces
- Spam complaints
- Unsubscribe requests
- Inactive users (180+ days)
- Role-based addresses (info@, sales@, admin@)
- Duplicate entries
Update your suppression list weekly and apply it before every send. Your email service provider should automatically suppress bounces and complaints, but manual reviews catch additional problem addresses their systems miss.
Step 6. Use Postmaster data in your marketing
Your google postmaster tools data becomes valuable only when you translate metrics into marketing decisions. You connect reputation scores directly to campaign performance, segment timing, and content strategy. Your deliverability data reveals patterns about what works and what damages your inbox placement, giving you concrete feedback loops for optimizing every email you send.
Connect dashboard metrics to campaign results
Match your Postmaster reputation changes to specific campaign send dates in your email platform. Download your spam rate data and overlay it with your campaign calendar to identify which messages triggered complaint spikes. Your domain reputation drops correlate with specific content types, subject line formulas, or audience segments that don’t resonate with recipients.
Create a campaign analysis template that combines both data sources:
Campaign: Holiday Sale Announcement
Send Date: 2025-12-15
Recipients: 45,000
Gmail Recipients: 28,000 (62%)
Postmaster Metrics (3 days post-send):
- Spam Rate: 0.18% (up from 0.08%)
- Domain Rep: High (unchanged)
- Delivery Errors: 45 (rate limiting)
Action Items:
- Remove urgency language from subject lines
- Reduce Gmail volume by 40% on next promotional send
- Test plain-text version with engaged segment
Your analysis reveals whether high-performing campaigns based on opens and clicks actually maintain good deliverability health. You discover that some campaigns generate strong engagement but also elevated spam complaints from specific subscriber segments.
Track your Gmail-specific metrics separately from your overall campaign analytics to optimize for deliverability, not just engagement rates.
Segment sends based on reputation windows
Your reputation scores fluctuate throughout the week based on sending patterns and subscriber behavior. Schedule your highest-value campaigns during periods when your domain reputation shows consistently High ratings. Save experimental content or re-engagement campaigns for times when a temporary reputation dip won’t impact critical business messages.
Build a sending priority system that protects your reputation during recovery periods. Send transactional emails and time-sensitive notifications first because they generate lower complaint rates than promotional content. Hold marketing blasts when your spam rate exceeds 0.15% until you identify and fix the underlying problem driving complaints.
Test content changes against spam metrics
Your spam complaint patterns reveal which content elements trigger negative reactions from Gmail users. Test alternative approaches for high-complaint campaigns by changing one variable at a time. Replace aggressive calls-to-action with softer language and measure whether your spam rate improves over the next three sends.
Run A/B tests where you track both engagement metrics and Postmaster data for each variation. Your control group might show higher open rates but also generate more spam complaints. Your test variation with plain-text formatting and minimal images could produce lower engagement but maintain cleaner reputation scores that improve long-term deliverability.
Bring it all together
You now have a complete system for monitoring and improving your Gmail deliverability using google postmaster tools. Start by verifying your domain and checking your authentication setup matches Gmail’s requirements. Review your dashboards weekly to catch problems before they damage your sender reputation. Use the metrics to guide your campaign decisions, content strategy, and sending patterns that maximize inbox placement.
Your deliverability success depends on consistent monitoring and quick responses to dashboard warnings. Set up your tracking spreadsheet today, schedule regular metric reviews, and connect your Postmaster data to actual campaign performance across all your email programs. Fix authentication failures immediately, reduce spam complaints through better list segmentation, and maintain steady sending patterns that Gmail rewards with consistent inbox delivery.
Strong deliverability creates opportunities, but converting those opportunities into paying customers requires specialized expertise. Client Factory builds conversion-optimized email campaigns that transform improved inbox placement into qualified leads and paying clients for service businesses.


